GS 1
Dangerous heat waves felt across globe as wildfires rage
Relevance: GS -1 Geography
Context: Heatwaves are affecting Asia, Europe, and the United States, showcasing the severe consequences of global warming.

Causes of Severe Heat Waves:
- Climate Change: Rising global temperatures due to greenhouse gas emissions contribute to the increased frequency and intensity of heatwaves.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Weather patterns and atmospheric pressure systems can trap hot air masses in specific regions, leading to prolonged heatwave events.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Urban areas, with their concrete and asphalt surfaces, absorb and retain heat, creating localized heat islands that intensify heatwaves.
Consequences of Heatwaves:
- Human Health Impacts: Heatwaves can result in heat exhaustion, heatstroke, dehydration, and other heat-related illnesses, especially among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
- Agricultural and Ecological Impacts: Heatwaves can lead to crop failures, reduced agricultural productivity, and stress on ecosystems. Heat stress can also harm wildlife, including fish and marine species.
- Infrastructure Challenges: Heatwaves can strain infrastructure, causing power outages, damaging roads and buildings, and increasing the demand for cooling systems.
Measures Taken to Address Heatwaves:
- Early Warning Systems: Governments and meteorological agencies are developing and implementing advanced forecasting systems to provide early warnings for heatwaves, allowing communities to prepare and take necessary precautions.
- Heatwave Emergency Plans: Local authorities are creating heatwave emergency plans that include the provision of cooling centers, increased public awareness, and outreach programs targeting vulnerable populations.
- Urban Planning and Green Infrastructure: Urban planners are incorporating green spaces, shade trees, and cool roofing materials to mitigate the urban heat island effect and provide relief during heatwaves.
- Building Design and Energy Efficiency: Building codes and regulations are being updated to enhance energy efficiency and promote the construction of heat-resilient structures.
- Heat-Health Action Plans: Health authorities are implementing heat-health action plans that involve public awareness campaigns, guidelines for healthcare professionals, and strategies to ensure access to cool shelters and adequate hydration.
Lightning not a natural disaster, says Centre
Relevance: GS Paper – 1 GS Paper – 3 Disaster Management
Context: The Union government in India is not in favor of declaring lightning as a natural disaster.
Lightning is a rapid and massive discharge of electricity in the atmosphere. It occurs due to the difference in electrical charge between clouds and the ground or within a cloud. Understanding the process and impact of lightning is crucial for safety and mitigating its harmful effects.
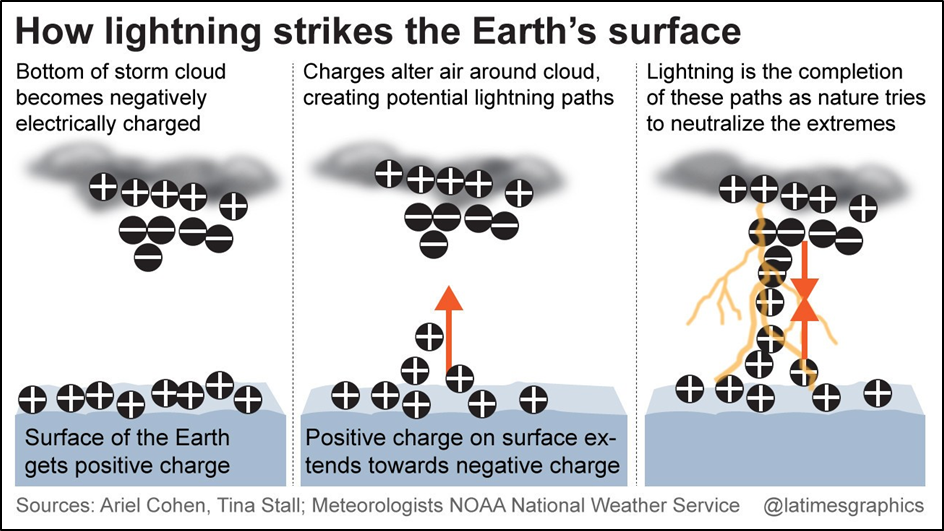
Lightning Process:
- Lightning occurs when electrical charges build up within a cloud, typically about 10-12 km in height, due to the movement and collision of ice crystals and water droplets.
- The collision of these particles leads to the release of electrons and the formation of a chain reaction, resulting in a large-scale flow of current between positively and negatively charged regions within the cloud.
- This current flow generates heat, causing the air column between cloud layers to expand rapidly, producing shock waves that result in thunder sounds.
Strikes Earth’s Surface:
- The Earth’s surface, being relatively positively charged compared to the middle layer of the cloud, attracts the current flow of lightning.
- Raised objects on the ground, such as trees and buildings, have a greater probability of being struck by lightning.
- Lightning conductors, commonly known as lightning rods, are installed on buildings to provide a path of least resistance for lightning to follow, protecting the structure from damage.
Climate Change and Lightning:
- Scientific studies suggest a link between climate change and increased incidences of lightning.
- Rising temperatures due to global warming can lead to a higher frequency of lightning strikes, with some studies indicating a 12% increase in strikes for every one-degree Celsius rise.
- The availability of more moisture over land as a result of climate change contributes to the heightened occurrence of lightning.
Lightning Strikes in India:
- India witnesses a significant number of lightning strikes each year, with millions recorded annually.
- The Lightning Resilient India Campaign (LRIC) aims to reduce lightning-related deaths and recorded 18.5 million strikes in India between April 2020 and March 2021, an increase of 34% compared to the previous year.
- Various organizations, including the Climate Resilient Observing-Systems Promotion Council and the India Meteorological Department, collaborate to raise awareness and implement measures to minimize lightning-related casualties.
GS 2
The Ukraine counter-offensive, a reality check
Context: The Ukrainian counteroffensive against Russia has faced challenges and has not achieved the expected success.
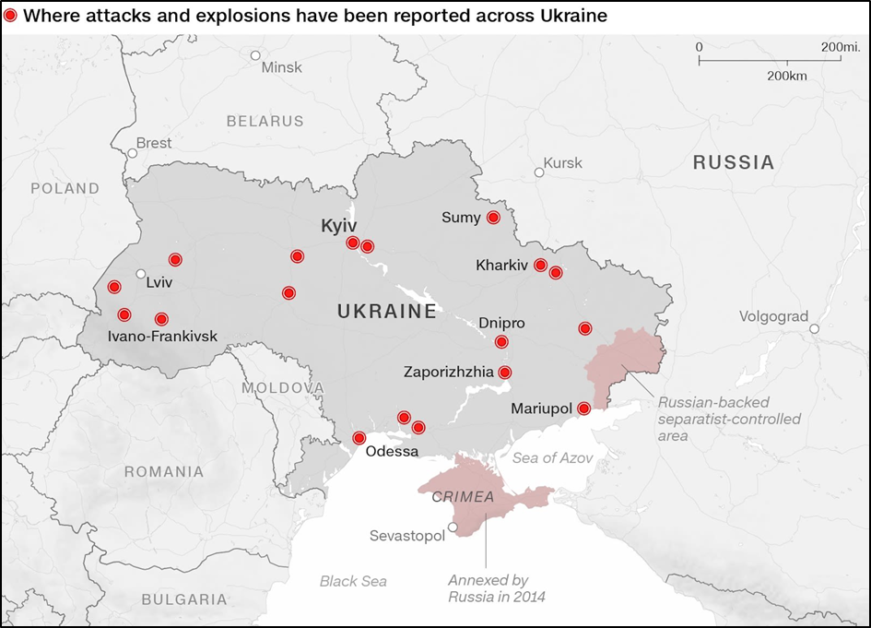
Ukrainian Offensive and Challenges:
- The Ukrainian counteroffensive, announced by President Volodymyr Zelenskyy on June 10, has faced difficulties in achieving its objectives.
- Despite assembling large quantities of NATO-supplied weaponry and troops, Ukraine lacks air supremacy and faces challenges in advancing on the ground.
- The revolt by the paramilitary mercenary Wagner Group against Russian military commanders has not provided the anticipated advantage to Ukraine.
Russian Defense and Adaptation:
- The Russian army has strengthened its defenses, dug in with heavily mined forward positions, and prepared for counter attacks.
- Russian equipment, considered by the West as antiquated, has been effectively utilized, countering Western perceptions.
- The Russian population appears ready for a protracted engagement, as NATO’s support for Ukraine suggests a total Russian defeat and evacuation of all Ukrainian territory.
NATO’s Involvement:
- The leaked Pentagon files revealed the presence of American, British, and other NATO fighters in Ukraine, but the numbers are still relatively small.
- While President Zelenskyy seeks additional weapons support, doubts arise regarding whether NATO’s resources will decisively impact the conflict.
- Prospects and Escalation:
- Prospects for a negotiated end to the war are receding, with a likelihood of escalation, particularly as the Ukrainian counteroffensive stalls and ammunition shortages become apparent.
- The U.S. decision to supply controversial cluster munitions to Ukraine raises concerns due to their impact on noncombatants and violation of the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
Flood feud
Context: Recent devastating floods in North India have brought attention to the complex relationship between climate change, urbanization, and infrastructural shortcomings in large Indian cities.
Unusual Flooding in Delhi:
- Delhi, a city not commonly associated with heavy rainfall, experienced excessive and record-breaking rain during the monsoon season.
- The city witnessed floods, even with reduced rainfall in recent days.
- The flooding has affected prominent landmarks and areas in the city, highlighting the potential disaster risks.
Factors Contributing to Flooding:
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Delhi’s infrastructural development has neglected measures to restrict construction on the floodplains of the Yamuna River, hindered proper drainage system maintenance, and allowed large-scale concretization.
- Yamuna River Management: The flooding is attributed to the overflowing of the Yamuna River, particularly due to the unregulated flow from upstream states like Haryana. The barrages in Delhi have been ineffective in managing the river’s flow.
Need for Collaborative Approach:
- Future Flood Threats: The increased probability of extreme rainfall events due to climate change in the Arctic and the Arabian Sea necessitates preparedness for more frequent flooding incidents.
- Joint Strategy: Similar to the collaborative approach taken to address air pollution, Delhi and the upstream states must set aside their differences and develop a joint strategy to counter future floods.
- Population Growth and Infrastructure: Delhi’s expanding population and infrastructure demands require a comprehensive approach that includes effective floodplain management, drainage system improvement, and sustainable urban planning.
India’s relationship with France is unique and multidimensional
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s recent visit to France marked the celebration of 25 years of the India-France strategic partnership.
Strategic Roadmap:
- The “Horizon 2047” roadmap was unveiled, outlining the strategic cooperation between India and France for the next 25 years. Areas of collaboration include defence, space, nuclear energy, climate change, green transitions, education, and people-to-people ties.
- Cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region was emphasized, including military and naval exchanges and the establishment of a trilateral development fund to assist countries in the region.
Defence Deals and Cooperation:
- Agreements were made to purchase 26 more Rafale fighter jets (Rafale-M) for the Indian Navy, continuing the procurement of 2008. Additionally, three more Scorpene submarines were agreed upon.
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited and Safran reached an agreement for helicopter engines.
- The defence cooperation between India and France highlights the strengthening ties in the defence sector.
Respect for Strategic Autonomy:
- The India-France relationship is built on mutual respect for each other’s strategic autonomy. France has refrained from commenting on India’s internal affairs or foreign policy choices.
- France’s non-participation in international sanctions against India for its nuclear tests and its support in supplying uranium for India’s reactors showcase their respectful approach.
Differentiated Partnership:
- Unlike other major partnerships, India and France have not pushed each other to join coalitions, groupings, or alliances they are part of. The focus is on bilateral cooperation.
- Both countries have demonstrated their commitment to nurturing the relationship based on their unique dynamics and shared success.
GS 3
Coral bleaching
Context: Impact of climate change on corals
Relevance: GS 3 Environment
Definition and Appearance of Bleaching:
- Bleaching occurs when corals lose their vibrant colors and turn white due to environmental stress.
- The visual change in color serves as an indicator that something has changed in the surrounding water conditions.
Factors Contributing to Bleaching:
- Changes in the ocean environment, such as rising temperatures, increased acidity, and excessive brightness, disrupt the symbiotic relationship between corals and zooxanthellae.
- As a result, zooxanthellae abandon the corals, causing them to fade and appear bleached. Prolonged stress can lead to coral death.
- Additional Stressors and Ecosystem Changes: Other stressors, including low tides, water pollution, and alterations in ecosystems due to the climate crisis, exacerbate the vulnerability of corals and increase the risk of bleaching.
- Impact of Unprecedented Global Temperatures: Record-breaking temperatures worldwide have placed various organisms, including humans, in dire situations. Corals are particularly susceptible to the effects of increased temperatures, leading to bleaching.
Types of Coral Reefs:
- Fringing Reefs: These reefs develop close to the shoreline, directly adjacent to the coastlines of islands or continents.
- Barrier Reefs: Barrier reefs are separated from the shoreline by a lagoon, with a larger distance between the reef and land compared to fringing reefs.
- Atolls: Atolls are circular or oval-shaped reefs surrounding a central lagoon. They are usually found in the open ocean and often mark the location of submerged volcanic islands.
- Patch Reefs: Patch reefs are smaller, isolated reefs that are not directly connected to larger reef systems. They can be found within lagoons or along the continental shelf.
Formation and Growth:
- Coral reefs form over long periods of time through the accumulation of calcium carbonate skeletons secreted by coral polyps.
- Coral polyps live in symbiosis with photosynthetic algae called zooxanthellae, which provide energy through photosynthesis and contribute to the vibrant colors of coral reefs.
Biodiversity and Importance:
- Coral reefs support one of the highest levels of biodiversity on Earth, providing habitats for a wide range of marine species.
- They offer protection to coastlines by reducing the impact of waves and storms, preventing erosion, and preserving shoreline stability.
- Coral reefs are important sources of income through tourism, fisheries, and the discovery of potential pharmaceutical compounds.
Prelims
Commonly found cicada species sheds foreign tag to embrace Indian identity
Context: A cicada species commonly found in South India has been given the Indian name Purana cheeveeda, derived from its Malayalam name Cheeveedu.
- This corrects the misidentification of the species as Purana tigrina, which was originally described in Malaysia in 1850.
- Identification based on Genitalia: The researchers in Kerala observed differences in the structure of male genitalia and operculum, leading to the identification and correction of the misidentified cicada species.
- Significance of Discovery: The gradual disappearance of cicadas from homesteads in South India may indicate a decline in soil quality and vegetation. Researchers caution that the dwindling presence of these insects could be a consequence of deteriorating environmental conditions.


